A Faster, Derivatization-Free Workflow for Formaldehyde Quantitation with Headspace-MRR
Formaldehyde quantitation is a critical requirement across regulated industries, but traditional gas chromatography (GC) workflows introduce significant time, complexity, and operational risk. GC methods typically rely on derivatization—chemical modification of formaldehyde—before analysis. This step alone can add 30–45 minutes of preparation time and introduces opportunities for error due to reagent instability and multi-step handling. Headspace-MRR offers a fundamentally different approach: direct, derivatization-free quantitation of formaldehyde vapor with high specificity, strong linearity, and dramatically shorter workflows.
Why does GC require derivatization for formaldehyde analysis?
Definition: Derivatization stabilizes formaldehyde for GC separation and detection, but requires multiple steps using reagents such as DNPH or PFBHA.
Detail: As shown in Table 1 of the application note, GC workflows require extensive preparation: homogenization or dilution, reaction with derivatizing chemicals, extraction, filtration, vial preparation, and injection equilibration. Each step adds time and increases variability, especially because derivatives degrade rapidly and require careful handling. GC runs then add another 15–25 minutes of instrument time.
Example: A single GC sample commonly requires 1.5–2 hours of total workflow time pre-analysis, not counting potential repeat injections or troubleshooting.
How does headspace-MRR eliminate the need for derivatization?
Definition: MRR directly measures gas-phase rotational transitions of formaldehyde vapor, removing the need for chemical modification.
Detail: Headspace-MRR leverages formaldehyde’s unique rotational fingerprint to deliver selective quantitation without chromatographic separation. Samples are diluted, equilibrated, and analyzed directly. There are no reagent ratios to optimize, no reaction times to control, and no cleanup steps. The workflow is fully automated after vial loading, with complete sample-to-result turnaround in under 45 minutes, including a 15-minute equilibration step.
- No derivatization or chemical modification
- Minimal sample handling
- Fully automated acquisition (~10 minutes per sample)
- Consistent, selective molecular identification via rotational signatures
Example: Compared to GC, headspace-MRR can save roughly 40–70 minutes per sample by eliminating derivatization and multi-stage preparation.
What challenges make formaldehyde difficult to quantify accurately?
Definition: Formaldehyde’s reactivity and volatility make it sensitive to preparation steps, reaction conditions, and matrix components.
Detail: Derivatives formed during GC preparation are unstable and can degrade if conditions deviate. Matrix components—especially in aqueous or complex solutions—can interfere with recovery, sensitivity, and reproducibility. Because multiple manual steps are required, human input becomes a major source of variability.
Example: Matrix interference and handling steps are among the largest contributors to GC error modes. Headspace-MRR avoids many of these issues by measuring vapor directly.
How does MRR achieve robust, reproducible formaldehyde quantitation?
Definition: MRR quantitation is based on measuring formaldehyde’s gas-phase rotational transitions, which scale linearly with vapor pressure.
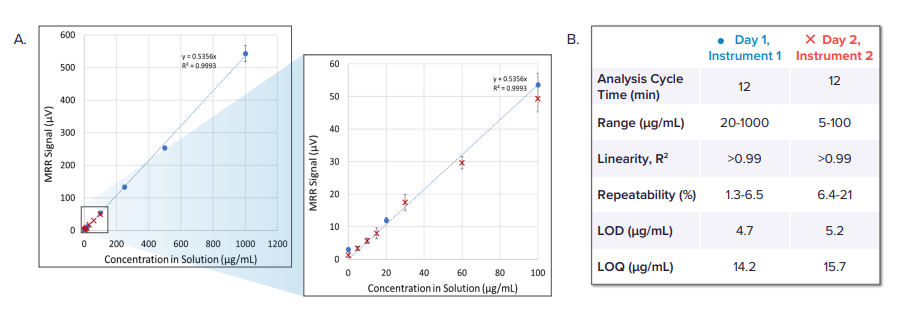
Detail: The application note demonstrates strong linear behavior across both low and wide concentration ranges. The calibration data show that MRR signal response is consistent across dilution series, with day-to-day and instrument-to-instrument variability remaining minimal. Even at 5 µg/mL, signals are measurable, and higher-concentration samples (up to 1000 µg/mL) show high signal-to-noise ratios.
Example: Users can tune sensitivity simply by adjusting scan time—longer acquisition allows lower limits of detection and quantitation without changing sample preparation.

What do the spectrum and calibration tables reveal about method performance?
Definition: MRR provides both spectral and quantitative evidence to validate selective formaldehyde detection.
Detail: The validated formaldehyde spectrum shows a strong peak at 14,488.48 MHz with high signal-to-noise for a 1000 µg/mL sample in a 50/50 excipient/water matrix. Quantitative tables summarize two calibration runs: Run 1 (20–1000 µg/mL) and Run 2 (5–100 µg/mL). Run 1 exhibits low RSD values, while Run 2 highlights expected increases in variability at the low end of detection.
Example: Even at the lowest concentrations in the calibration series, formaldehyde remains quantifiable, with precision further improved by increasing scan time.
How long does a full headspace-MRR workflow take?
Definition: MRR workflows are streamlined because they require only dilution, equilibration, and automated measurement.
Detail: Based on the workflow diagram, GC typically requires sequential steps including homogenization or dilution, derivatization, extraction, filtration, vial preparation, equilibration, and a 15–25 minute run. MRR requires only:
- Sample dilution (about 5–15 minutes)
- Approximately 15 minutes of headspace equilibration
- About 10 minutes of automated analysis
Example: The total time savings per sample can be approximately 40–70 minutes compared to GC derivatization workflows.
What makes MRR scalable for high-throughput environments?
Definition: MRR’s automation minimizes operator input and supports multi-instrument reproducibility.
Detail: The simplified workflow allows operators to load vials, select a target molecule, set acquisition parameters, and start automated measurement from an autosampler lineup. Day-to-day stability across instruments suggests strong suitability for large QA/QC labs that run many samples.
- Walk-away automation with autosamplers
- Minimal manual handling and fewer opportunities for error
- Consistent cross-instrument performance for multi-site deployment
Example: Labs analyzing many samples per batch can reduce hands-on labor while maintaining analytical rigor and strong quantitation performance.
Conclusion: Why switch to derivatization-free formaldehyde analysis?
Headspace-MRR provides a modern approach to formaldehyde quantitation. It dramatically cuts analysis time, eliminates derivatization and cleanup steps, and delivers reliable low-ppm detection with strong linearity and repeatability. Whether formaldehyde testing is used for process monitoring, materials testing, or routine QC, MRR offers a cleaner, faster, and more scalable alternative to GC-based methods—without sacrificing accuracy or selectivity.